ONS Retail Sales September 2020
Retail sales (value, non-seasonally adjusted, excluding fuel) increased for a fourth consecutive month in September, up by 5.8% year-on-year according to the latest ONS data.
Lifestyle changes and restricted opportunities to spend on leisure has seen a transference of spending to the benefit of grocery and home-related categories in recent months.
In volume terms (seasonally adjusted, excluding fuel), this marked a 6.4% increase in September on last year and 1.6% increase on last month.
Such has been the pace of recovery in retail that the three months to September has seen retail sales volumes increasing by 14.5% compared with the previous three months – marginally down on the record 15.5% in the previous month.
This saw retail sales volumes stand at 7.0% higher compared with February’s pre-pandemic level.
Retail sales (volume, seasonally adjusted) – 3-months on previous 3-months
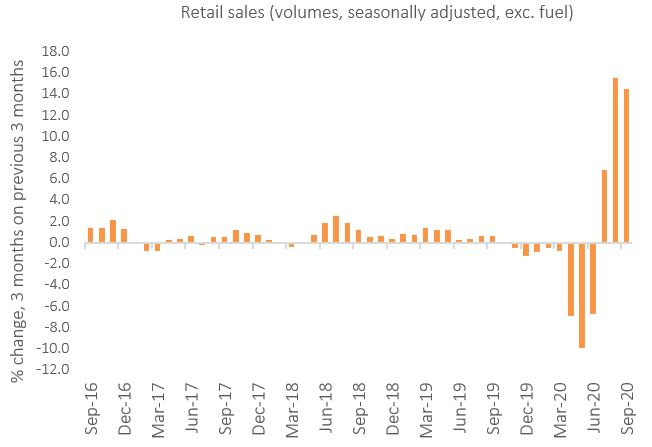
Source: ONS
Breaking down the performance, the ONS noted that non-food store sales were 1.7% above their February levels in September. Non-food has faced a slower recovery compared to retail overall as its performance is polarised by the renewed focus on home-related goods and distress among apparel.
Local lockdowns and restrictions on gatherings are likely to undermine the recovery of certain non-food categories such as clothing over the festive period.
As consumers ultimately go out less, the recovery in retail is favouring online players. Online sales (non-seasonally adjusted, excluding automotive fuel) were up by 52.6% year-on-year in September. While this is down on the recent peak of 73.1% online growth recorded in June, online sales accounted for 26.1% of total retail sales in September compared to 18.1% a year earlier.
The retail sales deflator (a measure of inflation specific to retail) excluding fuel was down 0.5% in September compared to last year, marking the largest decline since October 2016. Including fuel, the deflate was down by 1.4%.
This came as the implied price deflator among non-food stores dipped for a second month, down by 0.7% year-on-year in September, while prices were flat in food stores.
Back to Retail Economic News